Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have become integral to modern business operations. However, many people still wonder: What does ERP mean? In this article, we will delve into the definition of ERP, its core functionalities, and its numerous benefits to businesses. Whether you’re a business owner, manager, or simply curious about ERP, this comprehensive guide will provide a solid understanding of ERP and its significance in today’s competitive landscape.
Defining ERP
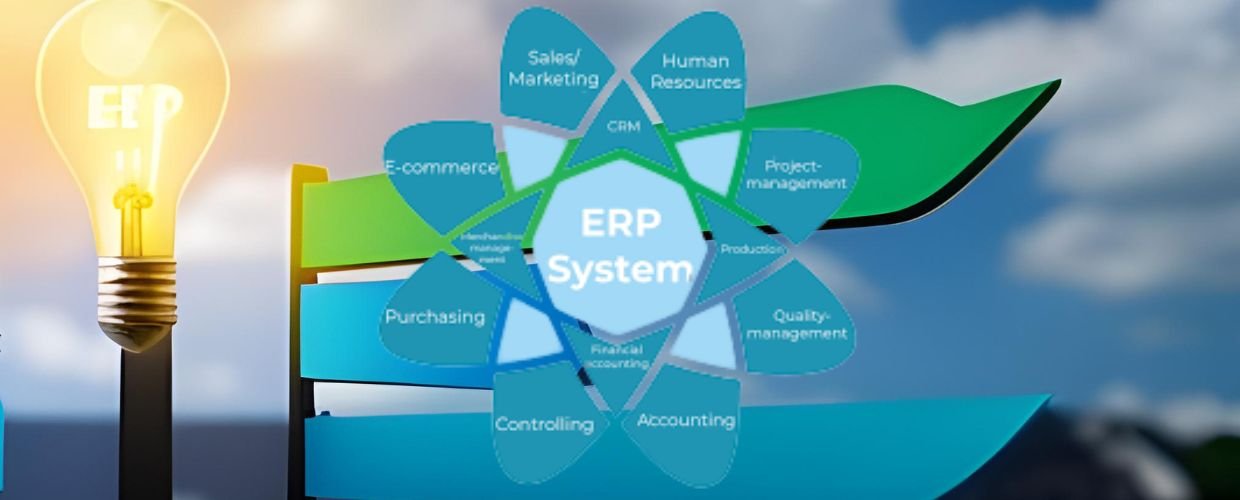
ERP is a suite of integrated software applications to manage and automate core business processes. These processes include finance, accounting, human resources, supply chain management, manufacturing, and customer relationship management. The primary objective of ERP is to streamline operations, enhance collaboration, and provide real-time visibility into various facets of an organization.
Its systems combine departments and functions within a company, ensuring they work together seamlessly and effectively to share data. Integrating these diverse processes into a unified approach eliminates data silos and enhances cross-functional communication and collaboration. This integration allows for a holistic view of the organization, enabling better decision-making, resource allocation, and strategic planning.
Core Functionality of ERP Systems
ERP systems encompass various modules, each catering to a specific aspect of business operations. Some common modules include financial management, inventory management, procurement, sales and marketing, production planning, and human resource management. These modules work together, sharing data and information seamlessly, ensuring that all departments within an organization have access to accurate and up-to-date information. This integration eliminates data duplication and discrepancies, facilitates efficient decision-making, and enables organizations to respond swiftly to changing market demands.
Financial management modules in ERP systems handle accounting, budgeting, financial reporting, and cash management. They automate routine financial processes, such as invoicing, payments, and reconciliation, streamlining financial operations and ensuring compliance with accounting standards and regulations. Inventory management modules enable organizations to effectively manage inventory levels, track stock movements, and optimize supply chain operations. With real-time visibility into inventory, businesses can avoid stockouts, reduce carrying costs, and improve order fulfillment.
Procurement modules automate the purchasing process, from requisitions to vendor management. They help streamline supplier selection, negotiate favorable terms, and manage procurement contracts. By centralizing procurement activities, systems enhance efficiency and control over the supply chain.
Sales and marketing modules in ERP systems aid in managing customer relationships, sales pipelines, and marketing campaigns. Organizations can gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and buying patterns by consolidating customer data. This information enables targeted marketing strategies, personalized customer interactions, and increased sales conversion rates.
Production planning modules optimize the manufacturing process by aligning production schedules with demand forecasts, managing bills of materials, and coordinating resources. It enables efficient resource utilization, minimizes production bottlenecks, and improves operational efficiency. Human resource management modules handle employee-related processes, including recruitment, onboarding, payroll, training, and performance management. Automating these tasks simplifies HR operations, reduces administrative burdens, and improves workforce productivity.
Benefits of ERP Systems
Implementing an ERP system offers several advantages for businesses. Firstly, it improves operational efficiency by automating manual tasks, reducing redundant processes, and minimizing errors. With streamlined workflows, organizations can save time and resources, allowing employees to focus on value-added activities. By eliminating time-consuming manual tasks, it systems enable employees to allocate their time and efforts to more strategic and innovative endeavors.
ERP systems enhance data visibility and integrity. Centralizing data eliminates data duplication and ensures that all departments work with consistent and reliable information. It promotes collaboration and enables managers to make informed decisions based on real-time data. Accurate and up-to-date information enables organizations to respond swiftly to market changes, make data-driven decisions, and proactively identify areas for improvement.
ERP systems facilitate better customer relationship management. With integrated customer data, organizations can track interactions, manage sales pipelines, and deliver personalized experiences. It leads to improved customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention. By understanding customer preferences and history, businesses can tailor their products, services, and marketing efforts to meet specific customer needs, fostering long-term relationships and customer loyalty.
ERP systems provide valuable insights through robust reporting and analytics capabilities. These tools enable businesses to generate customized reports, monitor key performance indicators, and identify trends and patterns. Such insights empower organizations to make data-driven decisions, optimize processes, and seize new opportunities. With real-time access to critical data, businesses can identify areas of improvement, optimize resource allocation, and align strategies with market demands.
Its systems contribute to regulatory compliance by enforcing standardized processes, ensuring accurate financial reporting, and maintaining data security. Organizations reduce the risk of errors, penalties, and legal consequences by automating compliance-related tasks, strengthening their reputation and credibility.
Implementation Challenges and Best Practices
Implementing an ERP system can be complex. It requires careful planning, effective change management, and strong leadership. Common challenges include resistance to change, data migration issues, and inadequate training. However, by following best practices, businesses can overcome these challenges and maximize the benefits of their implementation.
One crucial aspect of successful ERP implementation is conducting a thorough needs assessment. It involves analyzing existing business processes, identifying pain points, and defining specific objectives and requirements. By understanding the organization’s unique needs, businesses can select an ERP system that aligns with their goals and drives operational efficiency.
Choosing the right ERP vendor is another critical factor in implementation success. Organizations should evaluate vendors based on their industry experience, expertise, track record, and support services. Partnering with a reliable and experienced vendor ensures a smooth implementation process, ongoing support, and access to necessary upgrades and enhancements.
Involving key stakeholders throughout the implementation process is essential for securing buy-in and fostering a culture of collaboration. Key stakeholders, including department heads, employees, and executives, should actively participate in its implementation selection, planning, and deployment phases. This involvement ensures that the system meets the needs of different departments, promotes ownership, and facilitates a smooth transition.
Comprehensive training is vital to empower employees to use the new ERP system effectively. Training programs should cover not only the technical aspects but also the benefits and importance of the system. By investing in employee training, businesses can enhance user adoption, reduce resistance to change, and maximize the return on investment.
Conclusion
In decision, ERP is a comprehensive suite of integrated software applications designed to streamline business operations and enhance collaboration. It offers a range of benefits, including increased operational efficiency, improved data visibility, enhanced customer relationship management, valuable insights for decision-making and regulatory compliance. While implementing an ERP system may present challenges, organizations that approach the process strategically and follow best practices can reap substantial rewards. As businesses evolve and grow, it will remain a critical tool for success in the modern business landscape.