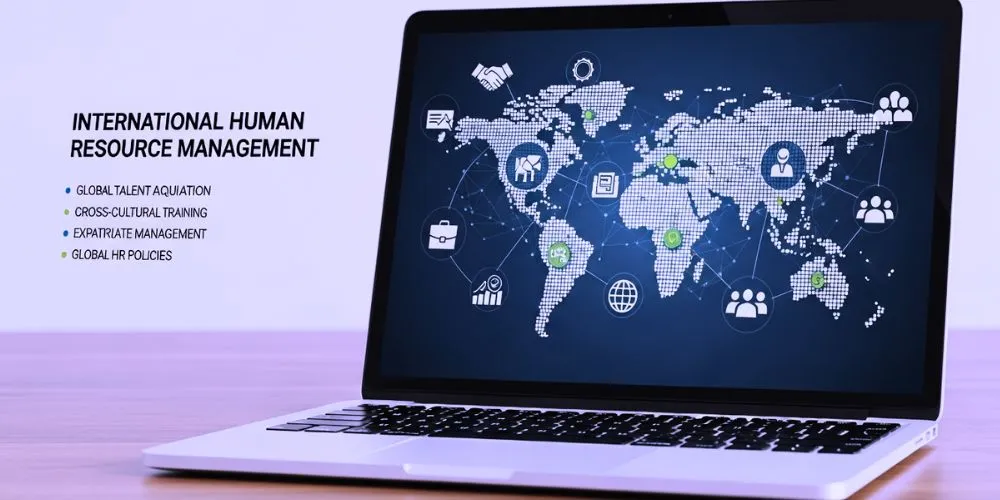
International Human Resource Management (IHRM) is a dynamic and strategic approach to managing a diverse global workforce. As organizations expand their operations across borders, International Human Resource Management plays a crucial role in ensuring the effective management of human capital in various cultural, legal, and economic contexts. In this article, we will explore the significance of IHRM, its key components, and the critical role it plays in navigating the ever-evolving global workforce landscape.
Understanding IHRM
IHRM focuses on managing human resources across borders and cultures. It involves designing HR strategies and policies that align with the global business strategy while considering each international location’s unique characteristics and needs. International Human Resource Management emphasizes adaptability, cultural sensitivity, and flexibility in dealing with a global workforce’s diverse challenges. International Human Resource Management goes beyond traditional HR practices, addressing the complexities and challenges of international staffing, employee development, cross-cultural communication, and global talent acquisition.
Critical Components of IHRM
International Human Resource Management is a complex and multifaceted field that requires a deep understanding of various critical components.
Global Talent Acquisition and Recruitment
One of the primary challenges for multinational organizations is identifying and recruiting talent from different countries and cultural backgrounds. IHRM professionals must understand the local labor markets, employment regulations, and immigration policies to attract the best candidates for international assignments. Talent acquisition strategies should consider the cultural fit and language proficiency required for successful integration into the host country’s work environment.
Expatriate Management
Managing expatriates, and employees assigned to work in foreign countries, is a critical aspect of IHRM. Sending employees to work abroad involves significant investments, and effective expatriate management is essential to ensure their success and maximize the return on investment. It includes pre-departure training to prepare expatriates for cultural and work-related challenges, ongoing support during their assignment, and reintegration assistance upon returning home country. Properly managed expatriates are more likely to adapt to the host country’s culture and work effectively, contributing positively to the organization’s success.
Cross-Cultural Training and Communication
IHRM emphasizes the need for cross-cultural training and communication to promote understanding and collaboration among a diverse workforce. Cultural intelligence and sensitivity are essential for building cohesive and high-performing global teams. Cross-cultural training helps employees and managers develop the necessary skills to navigate cultural differences, avoid misunderstandings, and work effectively in multicultural environments.
Global Compensation and Benefits
IHRM addresses the complexities of global compensation and benefits. It involves aligning compensation packages with local market standards while ensuring equitable and fair remuneration across different countries. The challenge lies in balancing the need to remain competitive in each regional market while maintaining internal equity and consistency across the organization.
International Employee Relations
Managing employee relations internationally requires a deep understanding of cultural norms, local labor laws, and practices. IHRM professionals mediate conflicts, promote cross-cultural understanding, and foster harmonious work environments. Effective employee relations practices increase employee satisfaction, productivity, and retention.
Compliance with International Laws and Regulations
International Human Resource Management ensures compliance with various international labor laws, employment regulations, and tax requirements. Adhering to legal and ethical standards is crucial for avoiding legal complications and maintaining a positive corporate image. IHRM professionals must stay updated on the ever-changing international regulations and ensure that the organization’s HR practices align with the local legal frameworks in each country of operation.
The Role of IHRM in the Global Workforce Landscape
The Role of International Human Resource Management in the Global Workforce Landscape cannot be overstated. Managing a diverse and geographically dispersed workforce requires a deep understanding of cultural awareness, language skills, legal compliance, and effective communication.
Strategic Alignment
IHRM aligns HR strategies with the organization’s global business objectives. By understanding the nuances of different markets and cultural contexts, IHRM contributes to successfully implementing the global business strategy. For example, IHRM may play a role in identifying potential growth markets, analyzing labor market conditions, and developing a talent pipeline to support expansion.
Talent Management and Development
IHRM identifies and nurtures top talent globally. Effective talent management ensures the organization has the right people in the right roles, regardless of geographical boundaries. It may involve creating career development pathways for employees in different countries, offering international assignments as part of talent development programs, and promoting diversity and inclusion across the organization.
Cultural Competence
IHRM cultivates cultural competence among employees and managers. Cross-cultural training and communication enable employees to collaborate effectively in multicultural teams, fostering innovation and creativity. Culturally competent leaders can leverage their global workforce’s diverse perspectives and strengths to drive organizational success.
Global Mobility
International Human Resource Management facilitates global mobility, enabling employees to take on international assignments and gain valuable cross-cultural experience. Global mobility programs enhance employee development and support talent retention. Employees who have had international experiences are often more adaptable, resilient, and better equipped to handle complex business challenges.
Risk Mitigation
International Human Resource Management minimizes managing a global workforce’s operational and legal risks. By staying informed about international regulations and compliance requirements, IHRM protects the organization from potential liabilities. For instance, IHRM may work closely with legal teams to ensure the organization’s policies comply with local labor laws and prevent legal disputes or penalties.
Conclusion
International Human Resource Management is a strategic imperative for organizations operating in the global business landscape. IHRM is pivotal in managing a diverse and multicultural workforce as businesses expand their operations across borders. By addressing the unique challenges of global talent acquisition, cross-cultural communication, and compliance with international laws, International Human Resource Management enables organizations to thrive in the interconnected and ever-changing world.
Embracing the principles of International Human Resource Management empowers businesses to navigate the complexities of the global workforce landscape and capitalize on the opportunities offered by international expansion. With a practical IHRM approach, organizations can attract, develop, and retain the best talent worldwide, fostering innovation, competitiveness, and sustainable growth in today’s global economy.