In today’s fast-paced business environment, enterprises require robust and versatile systems to manage their operations efficiently. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems offer a comprehensive solution by integrating various business functions and processes through modular components known as ERP modules. In this article, we will delve deeper into the significance of ERP modules, explore their key functionalities, and understand their impact on enhancing overall business efficiency and performance.
Understanding ERP Modules
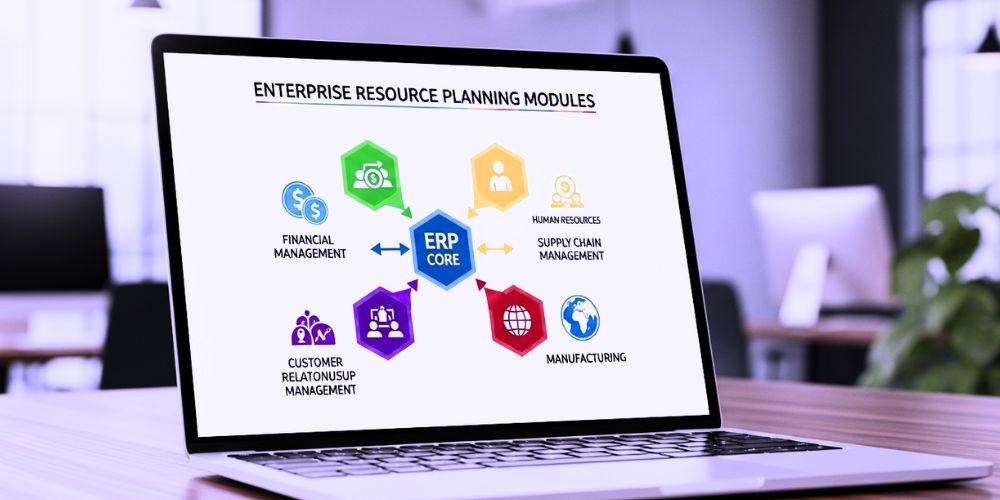
An ERP system is a suite of integrated software applications designed to streamline business processes, enhance collaboration, and optimize resource utilization. The core strength of an ERP system lies in its modular architecture, where each module addresses a specific business function or department. Organizations can choose and customize these modules based on their unique requirements, ensuring a tailor-made ERP system that aligns with their operations. These modules work in tandem to facilitate seamless data flow, automate tasks, and provide real-time insights for informed decision-making.
Key ERP Modules and Their Functionalities
Regarding ERP systems, several vital modules are essential to the smooth functioning of any organization.
Finance Module
The finance module is the backbone of an ERP system, handling all financial transactions, accounting processes, and financial reporting. It comprises various sub-modules such as general ledger, accounts payable and receivable, budgeting, fixed asset management, and financial analysis. The finance module ensures accuracy and transparency in economic data, enabling organizations to make well-informed financial decisions, comply with regulatory requirements, and effectively manage budgets.
Human Resources Module
The human resources module centralizes employee data and automates HR processes, simplifying workforce management. It includes functionalities such as payroll processing, time and attendance tracking, performance management, recruitment and applicant tracking, training and development, and benefits administration. The HR module streamlines HR operations, enhances employee engagement, supports talent management strategies, and promotes compliance with labor laws and regulations.
Sales and Distribution Module
The sales and distribution module focuses on managing the entire sales process, from order processing and sales forecasting to inventory management and customer relationship management (CRM). It tracks sales transactions, manages customer data, streamlines the order-to-cash process, and improves sales efficiency and customer satisfaction. The module also integrates with other ERP modules, such as inventory management and finance, to provide a holistic view of the sales pipeline and financial impact.
Manufacturing Module
The manufacturing module is vital for organizations involved in production and manufacturing activities. It facilitates production, material requirements planning (MRP), shop floor control, and quality management. By optimizing production schedules, tracking work-in-progress, and ensuring quality control, the manufacturing module leads to improved manufacturing efficiency, reduced costs, and better production output.
Inventory Management Module
The inventory management module is crucial in maintaining optimal stock levels, managing inventory movements, and minimizing carrying costs. It enables organizations to track stock levels in real-time, automate replenishment processes, and optimize reorder points to prevent stockouts and overstocking. This module helps businesses maintain adequate inventory levels for smooth operations while minimizing inventory holding costs.
Procurement Module
The procurement module streamlines the procurement process by managing supplier selection, purchase requisitions, purchase orders, and supplier performance evaluation. It helps organizations improve procurement efficiency, reduce purchasing cycle times, negotiate better terms with suppliers, and enhance collaboration. By centralizing procurement activities, this module ensures better control over spending and improves transparency in the procurement process.
Project Management Module
The project management module enables organizations to plan, execute, and monitor projects efficiently. It assists in resource allocation, project progress tracking, cost management, and risk assessment. The module ensures that projects are delivered on time, within budget, and meet the defined scope, fostering successful project outcomes and client satisfaction.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Module
The CRM module manages customer interactions, sales leads, and marketing campaigns. It centralizes customer data, automates sales processes, and supports personalized customer engagement. The CRM module is pivotal in driving business growth and enhancing brand loyalty by nurturing customer relationships, improving customer satisfaction, and increasing customer retention.
The Impact of ERP Modules on Business Efficiency
The integration of ERP modules into business operations can have a significant impact on overall efficiency.
Seamless Data Integration
One of the primary advantages of ERP modules is their ability to eliminate data silos by integrating information from various departments and functions. This seamless data integration ensures all stakeholders access a unified view of business processes, enabling them to make well-coordinated decisions based on real-time and accurate data.
Streamlined Processes and Automation
ERP modules automate repetitive and time-consuming tasks, reducing manual errors and increasing operational efficiency. By streamlining processes, organizations can achieve faster response times, reduced lead times, and improved resource utilization. Automation also saves costs by optimizing resource allocation and eliminating redundant operations.
Real-Time Insights for Decision-Making
ERP modules provide real-time data and insights, empowering organizations to make data-driven decisions. With access to up-to-date information, management can respond quickly to changing market conditions, identify potential bottlenecks, and optimize business strategies for increased competitiveness.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
ERP modules promote collaboration across departments by providing a centralized platform for sharing information and documents. It enhances communication, facilitates cross-functional cooperation, and fosters a culture of teamwork within the organization. Employees can access information relevant to their roles, leading to better collaboration and more informed decision-making.
Conclusion
ERP modules are the foundation of integrated business management, offering a comprehensive and unified platform for data management, process automation, and strategic decision-making. These modules cover diverse functional areas, from finance and human resources to sales, distribution, and manufacturing, fostering efficiency, collaboration, and data-driven insights. Embracing ERP modules as part of an integrated ERP system empowers businesses to stay agile, competitive, and well-equipped to adapt to the ever-changing demands of the modern business landscape. By harnessing the power of ERP modules, organizations can enhance overall business efficiency and drive sustainable growth in a dynamic and highly competitive market.