In the age of data-driven decision-making, organizations rely on Business Intelligence (BI) processes to extract valuable insights from their vast datasets. The BI process encompasses steps and methodologies to transform raw data into meaningful information that can drive strategic actions. The BI process empowers organizations to make informed decisions and gain a competitive edge by leveraging data collection, analysis, visualization, and reporting techniques. This article explores the concept of the BI process, its key components, and its transformative impact on organizations.
Understanding the BI Process
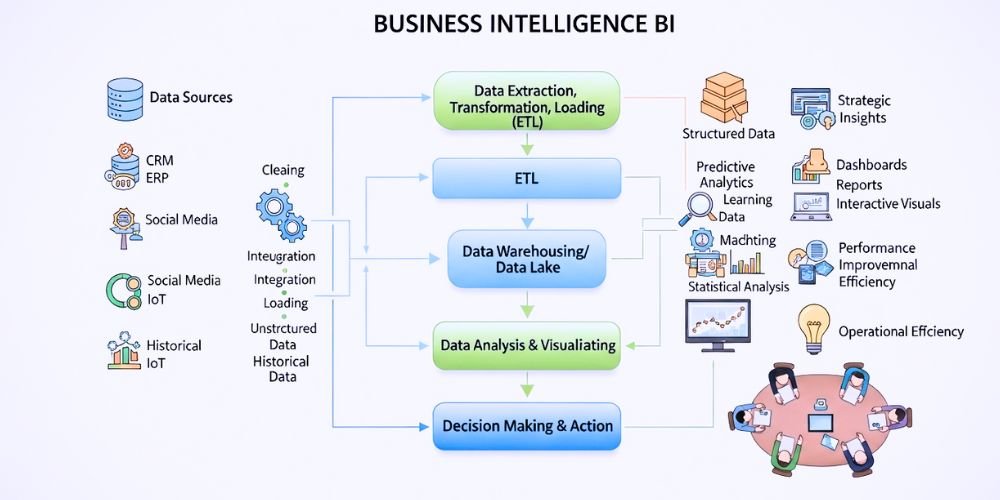
The BI process is a systematic approach that enables organizations to convert raw data into actionable insights. It involves a series of steps encompassing data collection, integration, analysis, visualization, and reporting. Organizations can transform data into meaningful information following a structured BI process, enabling stakeholders to make informed decisions and drive organizational success.
Key Components of the BI Process
Regarding the BI process, key components include data collection, analysis, and visualization. These crucial steps are necessary to gain valuable insights and create informed decisions based on data.
Data Collection
The BI process begins with data collection. Organizations gather data from various sources, including internal databases, external sources, cloud services, and APIs. Data can be structured (e.g., databases, spreadsheets) or unstructured (e.g., social media, emails). Effective data collection involves identifying relevant data sources, ensuring data quality, and implementing data governance practices to maintain accuracy, consistency, and integrity.
Data Integration
After data collection, the next step is data integration. Organizations consolidate and combine data from multiple sources into a central data repository or data warehouse. Data integration involves cleansing, transforming, and mapping to ensure consistency and compatibility across different data sets. By integrating data, organizations can create a unified view of the data, eliminating silos and enabling holistic analysis.
Data Analysis
Data analysis is a crucial component of the BI process. It involves applying various analytical techniques to uncover data patterns, trends, and insights. Data analysis techniques may include descriptive analytics (summarizing and visualizing data), diagnostic analytics (identifying causes of specific outcomes), predictive analytics (forecasting future trends), and prescriptive analytics (recommendations for optimal actions). Organizations gain useful insights into customer behavior, market trends, operational performance, and other key metrics through data analysis.
Data Visualization
Data visualization presents data in visual formats such as charts, graphs, and dashboards. Visualization simplifies complex information, making it easier to understand and interpret. Effective data visualization highlights patterns, trends, and relationships within the data, enabling stakeholders to grasp insights quickly. Interactive visualizations allow users to explore and drill down into specific details, further enhancing data understanding and decision-making.
Reporting and Distribution
Reporting is the final stage of the BI process, where insights and findings are shared with relevant stakeholders. Reports can take various forms, including static reports, interactive dashboards, and ad hoc reports. Accounts provide a concise summary of the insights derived from data analysis and visualization. Timely and accurate reporting enables stakeholders to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions based on the insights provided.
Impact of the BI Process
The impact of the BI process must be balanced. With the ability to collect, analyze, and visualize data, businesses can make informed decisions that greatly improve their operations and bottom line.
- Data-Driven Decision-Making: The BI process empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions. By analyzing and visualizing data, organizations gain insights that inform strategic actions. Data-driven decision-making reduces reliance on intuition and guesswork, increasing the accuracy and effectiveness of decision-making processes.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: The BI process enhances operational efficiency by identifying areas of improvement and optimizing processes. Data analysis can uncover organizational bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and waste areas. Organizations can streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve overall performance by addressing these issues.
- Enhanced Business Performance: The BI process enables organizations to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and track progress toward goals. With data visualization and reporting, organizations can identify trends, assess performance, and take corrective actions when necessary. It leads to improved business performance, increased productivity, and better alignment with strategic objectives.
- Competitive Advantage: Implementing a robust BI process provides a competitive advantage. Organizations can identify emerging market trends, customer preferences, and competitive threats by leveraging data insights. This knowledge allows organizations to adapt quickly, innovate, and stay ahead of the competition.
- Continuous Improvement: The BI process fosters a culture of continuous improvement within organizations—regular data analysis and reporting highlight areas for optimization and innovation. Organizations can continuously refine their strategies and techniques for ongoing success by monitoring performance, setting benchmarks, and tracking progress.
Conclusion
The BI process is a powerful framework that enables organizations to unlock the value of their data and make informed decisions. Organizations gain insights that drive strategic actions by collecting, integrating, analyzing, visualizing, and reporting data. It enhances decision-making, improves operational efficiency, enhances business performance, provides a competitive advantage, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement. In today’s data-driven world, organizations that embrace the BI process are better equipped to thrive in dynamic and competitive markets.